Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Battery Specifications
- 3. Calculating Battery Capacity
- Formula for Calculating Battery Capacity in Watt-hours (Wh)
- Example Calculation for a Single 12V 100Ah Battery
- 4. Parallel Battery Configuration
- 5. Runtime Calculation
- 6. Factors Affecting Battery Life
- 7. Practical Applications
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction
Overview of 12V 100Ah Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries, particularly the 12V 100Ah type, have become a cornerstone in modern energy storage solutions. Known for their high energy density, long lifespan, and lightweight design, these batteries are widely used in applications ranging from recreational vehicles (RVs) and marine systems to solar power setups and backup power supplies. The lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry, in particular, offers enhanced safety and stability, making it a preferred choice over traditional lead-acid batteries.
Importance of Understanding Battery Life
Understanding the lifespan and runtime of batteries is crucial for efficient energy management. Whether you're planning an off-grid adventure or setting up a reliable backup power system, knowing how long your batteries will last under specific conditions helps in optimizing their usage and ensuring uninterrupted power supply. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive guide on calculating the runtime of 4 parallel 12V 100Ah lithium batteries, considering various factors that influence battery life.
2. Understanding Battery Specifications
Definition of Amp-Hours (Ah) and Voltage (V)
The capacity of a battery is typically measured in amp-hours (Ah), which indicates the amount of current a battery can supply over a specific period. For instance, a 100Ah battery can deliver 100 amps for one hour or 10 amps for 10 hours. Voltage (V), on the other hand, refers to the electrical potential difference between two points. A 12V battery provides a consistent output of 12 volts.
Explanation of Lithium Battery Chemistry (LiFePO4)
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery known for their stability and safety. Unlike other lithium chemistries, LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to overheating and thermal runaway, making them ideal for high-demand applications. They offer a longer cycle life, typically ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 cycles, and maintain a steady voltage output throughout their discharge cycle.
3. Calculating Battery Capacity
Formula for Calculating Battery Capacity in Watt-hours (Wh)
To determine the energy capacity of a battery in watt-hours (Wh), you multiply the amp-hour (Ah) rating by the voltage (V). The formula is:
Example Calculation for a Single 12V 100Ah Battery
For a single 12V 100Ah battery, the capacity is calculated as follows:
This means the battery can theoretically provide 1200 watt-hours of energy.
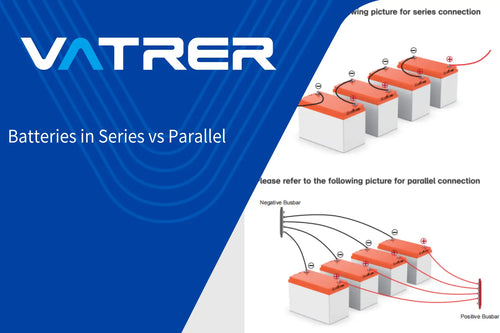
4. Parallel Battery Configuration
Explanation of Parallel Configuration
In a parallel configuration, multiple batteries are connected to increase the total capacity while maintaining the same voltage. When batteries are connected in parallel, their amp-hour ratings are summed, but the voltage remains unchanged.
Impact on Total Capacity and Voltage
For 4 parallel 12V 100Ah batteries, the total capacity is:
The voltage remains at 12V, but the total capacity increases to 4800Wh (400Ah × 12V).

5. Runtime Calculation
Formula for Calculating Runtime Based on Load
The runtime of a battery system can be calculated using the formula:
Example Scenarios with Different Power Requirements
-
Scenario 1: 400W Load
-
Scenario 2: 1000W Load
These calculations illustrate how the runtime varies with different power demands.
6. Factors Affecting Battery Life
Load Variations
The actual runtime can vary based on the load's consistency. Fluctuating loads can lead to shorter runtimes due to inefficiencies in power conversion and distribution.
Temperature and Environmental Conditions
Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance. High temperatures may increase the rate of chemical reactions within the battery, leading to faster discharge, while low temperatures can reduce the battery's capacity.
Battery Age and Cycle Life
As batteries age, their capacity diminishes. The number of charge-discharge cycles also impacts the overall lifespan. LiFePO4 batteries, with their high cycle life, offer better longevity compared to other types.
7. Practical Applications
Use Cases for 4 Parallel 12V 100Ah Batteries
-
Off-Grid Solar Systems: Providing reliable energy storage for solar power setups.
-
Recreational Vehicles (RVs): Ensuring extended power supply for appliances and electronics.
-
Marine Applications: Powering trolling motors and onboard systems for boats.
Benefits and Limitations
The primary benefit of using 4 parallel 12V 100Ah batteries is the increased capacity, allowing for longer runtimes and greater energy availability. However, the initial cost and space requirements can be a limitation for some users.
8. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Understanding the specifications and configurations of lithium batteries is essential for optimizing their use. By calculating the total capacity and considering factors like load and environmental conditions, users can effectively manage their energy needs.
Recommendations for Optimizing Battery Usage
To maximize the lifespan and efficiency of your battery system, consider the following:
-
Regularly monitor and manage the load to prevent over-discharge.
-
Store and operate batteries within recommended temperature ranges.
-
Perform routine maintenance and check for signs of wear or damage.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your 4 parallel 12V 100Ah lithium batteries provide reliable and long-lasting power for your applications.